At a Glance:
Biotin (Vitamin B7) helps strengthen hair, nails, and skin by supporting keratin production. It can improve thinning or brittle hair caused by a deficiency, but it isn’t a miracle growth supplement. Most adults need around 30 mcg a day, which can come from foods like eggs, nuts, and avocados. High doses (such as 10,000 mcg) aren’t proven to be more effective and may affect lab results.
Biotin, also known as Vitamin B7, is a water-soluble B-vitamin essential for maintaining healthy hair, skin, and nails. Often called the “beauty vitamin,” biotin is widely celebrated in the beauty and wellness industry for its benefits in supporting hair growth, strength, and overall vitality.
Many people turn to biotin supplements hoping to achieve fuller, thicker hair—but does biotin really help hair growth? And how much biotin should you take per day for the best results?
In this article, we’ll explore the science behind biotin’s effects on hair growth, discuss the recommended daily intake, and explain how biotin benefits not only your hair but your overall health—helping you decide if it’s the right choice for your hair care journey.
What is Biotin?
Biotin (Vitamin B7) is part of the B-complex family that helps convert nutrients into energy and supports keratin production—a key protein that forms your hair, skin, and nails.
Because keratin is essential for strong, healthy hair, biotin has become a popular supplement among people experiencing thinning or brittle hair.
A biotin deficiency can lead to symptoms like hair loss, brittle nails, and dry skin. However, most people can get sufficient amounts through a balanced diet containing biotin-rich foods like eggs, nuts, seeds, and avocados.
What does research say about biotin and hair growth?
Biotin contributes to keratin infrastructure, which is critical for hair strength and structure. Some studies suggest that people with biotin deficiency experience improved hair thickness and reduced shedding after supplementation.
For example, a clinical study reported improved hair growth and volume in women taking a multi-nutrient marine-protein supplement containing biotin for 90 to 180 days, though biotin was not tested in isolation. 1
However, it’s essential to note that biotin doesn’t directly cause hair growth in individuals who already have sufficient levels. Its main benefit lies in correcting deficiencies that may contribute to hair thinning or brittle hair.
In summary, while biotin supports overall hair health, research doesn’t conclusively show it as a miracle growth booster—but it may help when a deficiency is present.
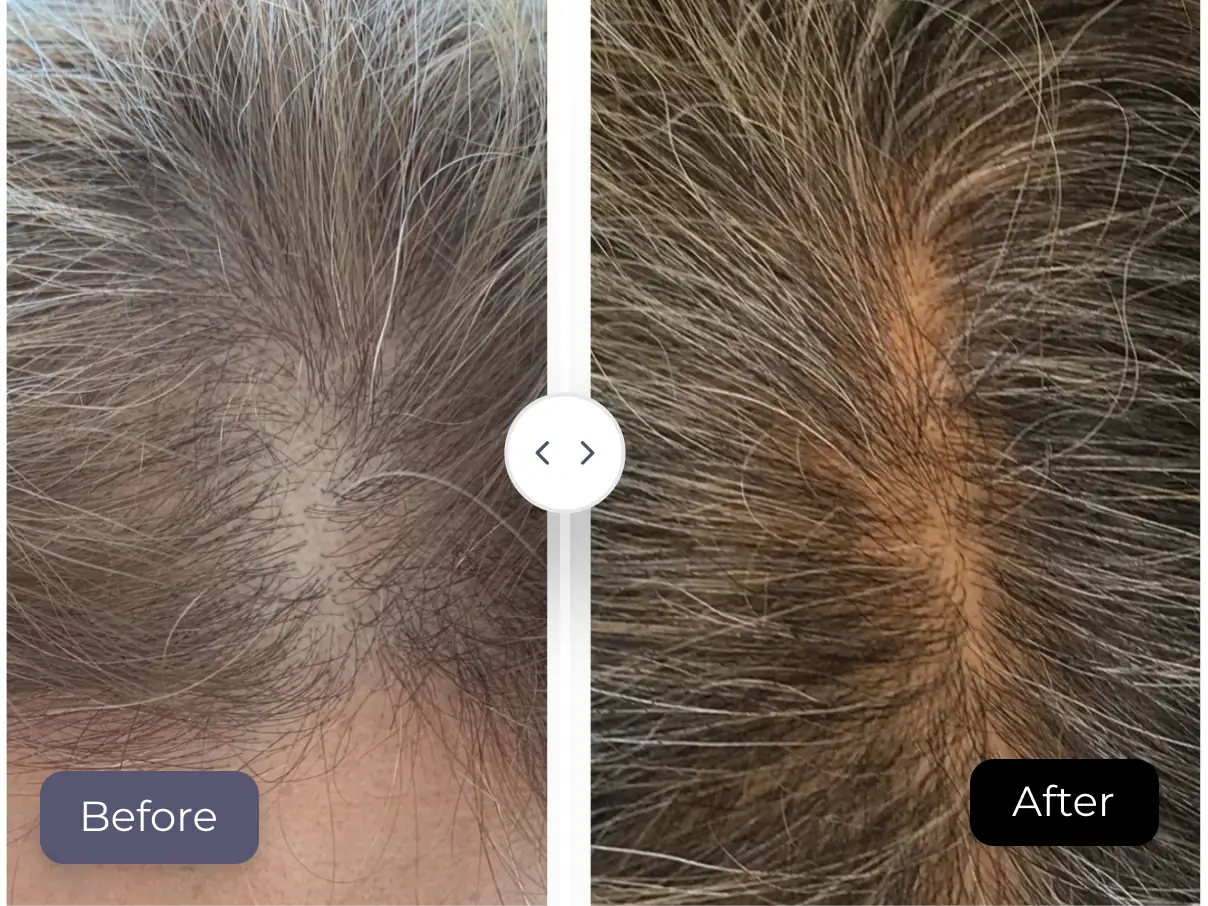
Does Biotin Help Hair Growth?
Many users take biotin supplements for hair loss, hoping for thicker, stronger hair. While evidence is limited, some individuals report noticeable improvements.
A study published in PubMed Central (PMC) revealed that 38% of women with hair loss had a biotin deficiency. When supplemented, these participants experienced improvements in hair and nail strength. 2
However, biotin alone can’t stop all types of hair loss, as factors like genetics, hormones, stress, and nutrition play significant roles.
If your hair loss is due to a deficiency, biotin supplementation or biotin-rich foods can help restore normal growth.
Who may be at risk for a biotin deficiency?
Biotin deficiency is uncommon but can affect specific groups, including:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- People with digestive disorders (like Crohn’s disease) that affect nutrient absorption
- Individuals consuming raw egg whites regularly (which contain avidin, a biotin-binding protein)
- Heavy smokers or drinkers, as alcohol can interfere with biotin absorption
- People on long-term antibiotics, which can alter gut bacteria responsible for biotin synthesis
If you fall into these categories, you might benefit from increasing biotin intake through food or supplements.
Causes of Biotin Deficiency
Biotin deficiency can result from:
- Poor Diet: Low intake of biotin-rich foods such as eggs, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
- Pregnancy or Lactation: These increase the body’s nutritional demands and may accelerate biotin metabolism.
- Medical Conditions: Disorders like liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or other malabsorption syndromes can impair biotin absorption.
- Raw Egg Whites: Overconsumption of raw eggs introduces avidin, a protein that binds to biotin and prevents its absorption.
- Genetic Causes: Biotinidase deficiency—a rare inherited condition—disrupts the body’s ability to recycle and utilize biotin.
Symptoms often include hair thinning, brittle nails, and dry, scaly skin.
How Much Biotin Should You Take
For most healthy adults, the recommended daily biotin intake is 30 micrograms (mcg). 3 If you’re considering supplements for hair growth, doses between 30–100 mcg per day are typically sufficient.
Is 10,000 mcg of biotin too much?
While 10,000 mcg (10 mg) supplements are widely marketed for hair growth, research doesn’t show added benefits beyond normal levels.
Excess biotin is usually excreted in urine, but very high doses can interfere with lab test results—including thyroid and heart tests.
Unless prescribed for a medical reason, stick to the recommended range and get additional biotin from dietary sources. 4
Biotin Side Effects
Biotin is considered safe and non-toxic, even at high doses, but potential side effects include:
Skin Rashes or Acne Breakouts
High doses may trigger mild skin irritation or acne due to imbalanced vitamin metabolism, especially between biotin and vitamin B5.
Digestive Discomfort
Some people experience mild nausea, cramping, or diarrhea when taking excessive biotin, especially on an empty stomach.
Rare Kidney Issues
Very high biotin doses may strain kidney function in sensitive individuals or those with pre-existing renal conditions.
Interference with Blood Tests
Large doses can distort thyroid or heart test results, leading to false readings. Always inform your doctor before testing.
To avoid complications, always inform your healthcare provider if you’re taking high-dose biotin before undergoing medical tests.

Does biotin shampoo help with hair growth?
Biotin shampoos and topical treatments are popular, but scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited. Biotin molecules are too large to penetrate deeply into the scalp or hair follicles, meaning they’re unlikely to stimulate actual growth.
However, biotin shampoos can improve the appearance of hair, making it look thicker and shinier by coating the strands and conditioning the scalp.
They may also help reduce breakage and dryness. For best results, combine topical care with dietary biotin intake or supplements when needed.
Biotin-Rich Foods for Boosting Hair Growth
Incorporating biotin-rich foods is one of the best natural ways to support hair health:
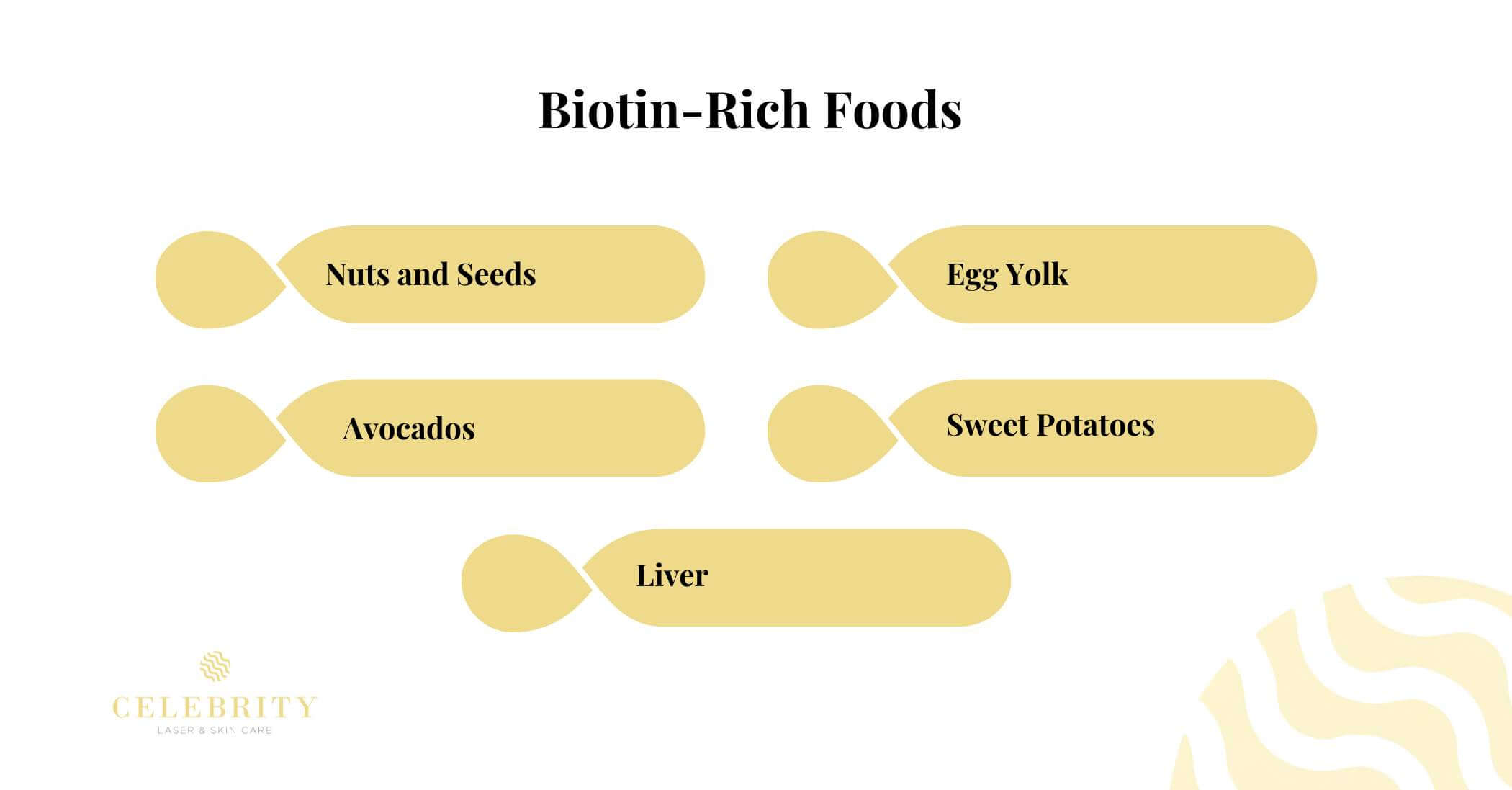
Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, sunflower seeds, pecans, walnuts, and peanuts are great sources of biotin. For example, a 1/4 cup of almonds contains 1.5 mcg, and sunflower seeds provide 2.6 mcg. Enjoy them raw, roasted, tossed in salads, or blended into nut butter for a delicious boost.
Avocados
Avocados are a nutrient-packed superfood. A medium avocado (about 7 ounces) offers approximately 1.85 mcg of biotin. Incorporate them into your diet by adding slices to salads, spreading them on toast, or making guacamole.
Egg Yolk
Egg yolks are rich in biotin, with one cooked egg providing up to 10 mcg. Avoid consuming raw egg whites, as they can block biotin absorption. Properly cooked eggs not only enhance absorption but also reduce the risk of Salmonella.
Sweet Potatoes
A 1/2 cup of cooked sweet potatoes offers 2.4 mcg of biotin, along with antioxidants that support scalp health and promote stronger, shinier hair.
Liver
The liver is one of the richest sources. Just 3 ounces of cooked beef liver provides 31 mcg, while chicken liver contains an impressive 138 mcg. Try it sautéed with onions, blended into burger patties, or served over pasta.
Other Natural Remedies for Hair Growth
While biotin supports hair health, combining it with other nutrients enhances results. Consider adding:
Vitamin D
Vitamin D helps regulate the hair growth cycle by stimulating new follicles and preventing premature shedding, promoting fuller, healthier hair.
Vitamin E
This antioxidant enhances blood flow to the scalp, delivering nutrients to hair follicles and protecting cells from oxidative damage.
Zinc and Iron
Zinc and iron support DNA synthesis and cell repair, helping hair follicles function properly and preventing thinning or brittleness.
Essential Oils
These oils may increase scalp circulation, strengthen follicles, and stimulate growth when massaged regularly into the scalp.
These nutrients, alongside a balanced diet, proper hydration, and stress management, create the best environment for healthy hair growth.
Conclusion
Biotin plays a crucial role in maintaining strong, vibrant hair, particularly for individuals with a biotin deficiency. It helps strengthen hair structure, reduce brittleness, and support overall scalp health.
However, biotin isn’t a miracle cure for baldness or severe hair loss—it works best when combined with a nutrient-rich diet and healthy lifestyle. Before starting any biotin supplement, consult your healthcare provider to determine the right dosage for your needs.
For personalized guidance and advanced wellness treatments, contact Celebrity Laser & Skin Care—your trusted partner in achieving radiant skin, hair, and confidence. Book now to start your customized treatment journey today.