At a Glance:
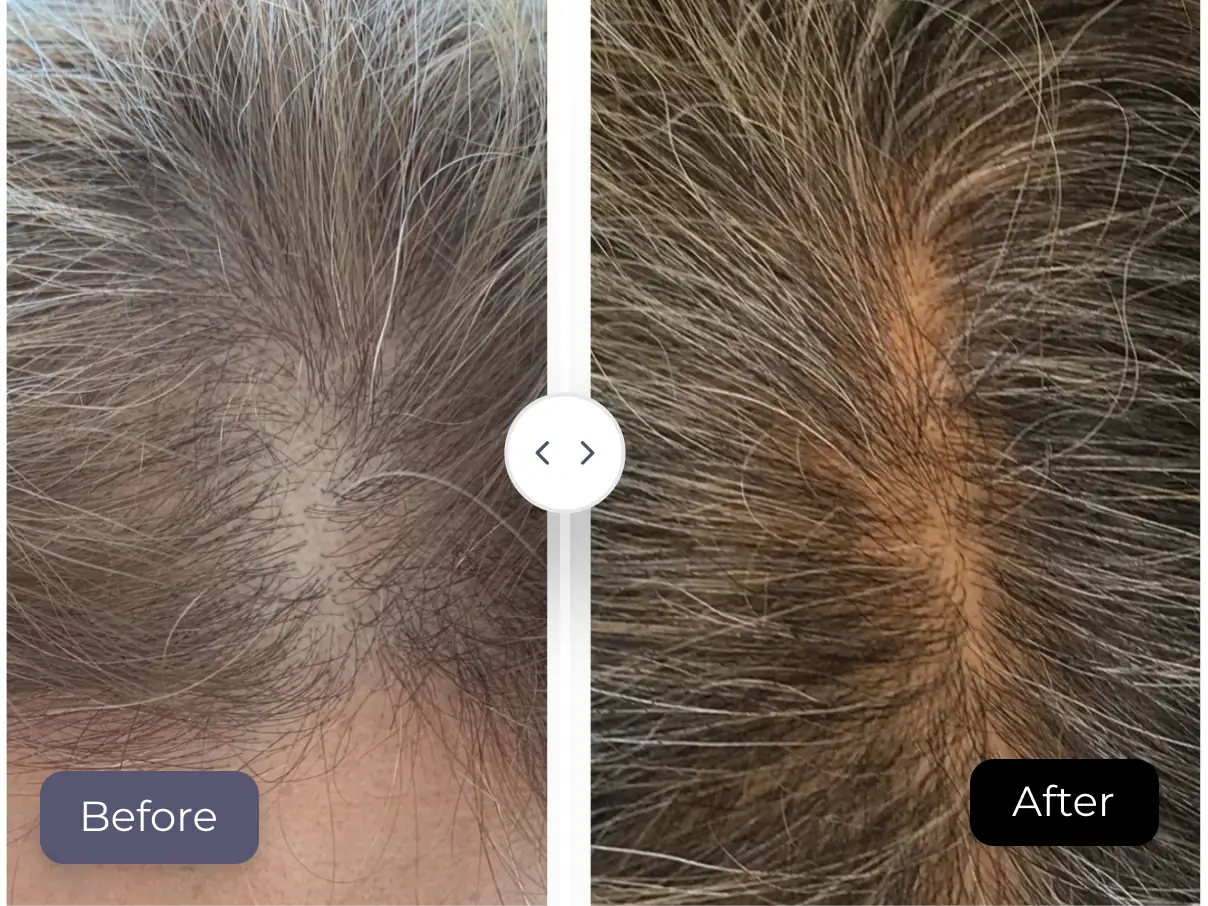
Paradoxical hypertrichosis is a rare side effect where clients notice excess hair growth after laser hair removal instead of reduction. It is more common in people with darker skin or fine facial hair, and usually develops within one to three months on areas such as the face, neck, or arms. The condition is typically not permanent and can be treated through advanced laser systems, electrolysis, or topical therapies.
Laser hair removal has become one of the most popular aesthetic treatments in Vancouver and across Canada, offering long-term reduction of unwanted hair with minimal discomfort. For most clients, the results are consistent and satisfying.
However, in rare cases, some people notice excess hair growth rather than a reduction. This phenomenon, known as paradoxical hypertrichosis (PH), may sound concerning, but it is uncommon and manageable with the right medical care.
At Celebrity Laser & Skin Care, we prioritize safety, accurate skin and hair assessments, and advanced technology to minimize risks and deliver effective solutions.
What is paradoxical hypertrichosis?
Paradoxical hypertrichosis refers to excess hair growth after laser hair removal, the opposite of the expected result. Instead of a hair reduction, some individuals notice new or thicker hair growth in the treated area or in the surrounding skin.
This effect is rare but real, and although it can be distressing, it is typically not permanent. Understanding the condition helps clients manage expectations and seek appropriate care.
How It Differs from Normal Regrowth
It’s crucial to distinguish paradoxical hypertrichosis from normal hair regrowth:
➤ Normal regrowth happens when hairs that were in a resting (telogen) phase at the time of treatment later cycle back into growth.
➤ Paradoxical hypertrichosis occurs when the laser appears to stimulate hair growth instead of reducing it, often resulting in thicker or darker hair than before.
What Causes Paradoxical Hypertrichosis After Laser Hair Removal
While the exact mechanism is still being studied, research and clinical experience have identified several post-laser hair growth causes:
Hair Stimulation Instead of Reduction
Low-level heat from the laser may not destroy the follicle but instead trigger it into activity. Instead of damaging the follicle enough to reduce growth, insufficient energy can cause hair stimulation after the laser.
Role of Skin and Hair Type
Certain skin and hair types are more prone to laser-induced hair growth:
➤ Darker skin types (higher Fitzpatrick classification) can absorb more energy, which may scatter into nearby follicles.
➤ Fine, light hairs (vellus hair) are particularly sensitive to this effect.
Laser Type and Energy Settings
The type of laser and its settings play a role. At Celebrity Laser & Skin Care, we use advanced platforms like Cutera Excel HR and Cutera Xeo, featuring Alexandrite 755 nm, Nd:YAG 1064 nm, and Prowave.
These lasers deliver precise energy to the follicle, safely targeting different skin tones while reducing the risk of paradoxical hypertrichosis and ensuring effective, lasting hair reduction.
Symptoms and Areas Most Affected
Paradoxical hypertrichosis usually presents in specific areas:
- Face and neck, particularly the lower face, in women
- Upper arms and shoulders
- Back and thighs
Symptoms may appear within one to three months after treatment. Clients often notice unwanted hair growth after laser treatment, typically around the edges of the treated area, where the laser energy was weaker.
Keep Reading: Paradoxical hypertrichosis can raise concerns about whether laser is always the right option. Some frequently asked questions include can pregnancy reverse laser hair removal and can you do laser hair removal over tattoos. Explore our articles for deeper insights.
Is It Permanent?
One of the most common concerns is whether paradoxical hypertrichosis is a permanent condition.
In most cases, the hair growth is not permanent. The condition can be reversed or improved with the right treatment plan. However, the outcome depends on:
- The type of laser used
- The number of sessions completed
- The individual’s hair and skin characteristics
With medical oversight and advanced technology, it is possible to reduce or even eliminate unwanted hair growth.
Treatment Options for Paradoxical Hypertrichosis
Clients experiencing this condition often ask, “How can paradoxical hypertrichosis be treated?” Several effective options exist:
Switching to a Different Laser Type
Adjusting the type of laser can significantly improve results, especially for clients with darker skin.
Electrolysis
For isolated resistant hairs, electrolysis may be a reliable alternative, as it destroys follicles individually using electrical current.
Topical Therapies
Prescription creams such as eflornithine can help slow hair growth in affected areas when used consistently.
Consultation and Treatment Re-Mapping
Re-assessing the treated area with an expert can help identify the exact cause of stimulation. With proper settings, follow-up treatments often bring the desired outcome.
How Celebrity Laser & Skin Care Handles Paradoxical Hypertrichosis
At Celebrity Laser & Skin Care, client safety and satisfaction are central to every treatment plan. The team takes proactive measures to reduce the risk of laser hair removal side effects, including paradoxical hypertrichosis.
Skin and Hair Assessment Before Treatment
Every client undergoes a detailed consultation during which their skin type, hair type, and medical history are reviewed. This helps in predicting potential risks and tailoring treatment accordingly.
Adjusted Laser Parameters for High-Risk Clients
The clinic’s advanced laser platforms allow precise adjustments of wavelength, pulse duration, and fluence. For clients at higher risk, settings are modified to reduce stimulation and increase efficacy.
Medical Oversight and Follow-Up Support
Treatments are carried out with medical oversight, ensuring that unexpected reactions like unwanted hair after laser treatment are promptly addressed. Clients receive ongoing support and, if needed, alternative treatment pathways.
Prevention Tips and Considerations
Reducing the risk of paradoxical hypertrichosis starts with choosing the right clinic.

Importance of Choosing the Right Clinic
Clinics with advanced technology and medical expertise are less likely to see complications. Celebrity Laser & Skin Care’s combination of medical training and advanced platforms offers clients a higher standard of care.
Laser hair removal performed by undertrained technicians or with outdated equipment carries a greater risk of side effects, including laser-induced hair growth.
Who Is at Higher Risk
Clients with:
- Darker skin tones
- Fine facial hair
- Hormonal conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
may be more likely to experience paradoxical hypertrichosis and should discuss this during consultation.
How to prepare for your first laser session?
Preparation plays a crucial role in both safety and achieving results. Clients are generally advised to avoid tanning, waxing, or plucking before treatment, and to shave the area 24 hours in advance.
At Celebrity Laser & Skin Care, we provide clear, personalized guidance on how to prepare for your first laser session, helping clients feel confident while lowering the risk of side effects.
Keep Reading: can hair laser removal cause cancer
Conclusion
Paradoxical hypertrichosis may sound alarming, but with proper care, it can be addressed effectively. The condition highlights the importance of seeking treatment from experienced providers who understand the nuances of laser technology and skin physiology.
If you are concerned about excess hair growth after laser hair removal or want expert advice before starting treatments, a consultation is the best first step.
At Celebrity Laser & Skin Care in North Vancouver, each treatment plan is customized to the individual. With advanced laser technology, medical guidance, and a focus on patient safety, the clinic offers a trusted environment for those seeking lasting results.